What's AI Art And Will AI Art Replace Artists?
KNOWLEDGE
The rise of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) left people wondering on its roles in the future.
Many speculated that creative industries that rely on creativity and imagination are the least susceptible
industries to automation. However, with the rise of AI art and AI tools, that doesn't seem to be the
case.
Today, AI not only actively imposes threat on literature and written art, it also rapidly advances in the realm of painting and visual art.
What exactly is AI art and how does AI create AI art? Will AI eventually replace human jobs entirely?
AI may be on the verge of ushering in a new era where we coexist with AI rather than being adversaries. By understanding AI, we can better harness its potential. In this article, we will explore the current state and future implications of AI across various dimensions.
History of AI art and how it has evolved over the years

The utilization of computers to create art has a history that spans several decades. In 1973, a significant milestone in AI art was reached with the development of "AARON," a computer program created by Harold Cohen capable of autonomously generating unique abstract artwork.
In 2015, Google introduced the DeepDream algorithm, which utilizes deep neural networks to generate intricate visual images by enhancing patterns and features within existing images.
In 2018, an artwork created by artificial intelligence called Portrait of Edmond Belamy, depicting a slightly blurred portrait of a man, was sold at auction for an astonishing price of $432,500. This value was 40 times higher than its estimated worth, showcasing the increasing global attention towards AI-generated paintings.
The sale of Portrait of Edmond Belamy, produced using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), represents a significant breakthrough for AI art, both in terms of recognition and commercial value.
Since then, AI art has flourished and has become a vibrant field where creativity, technology, and machine learning intersect.
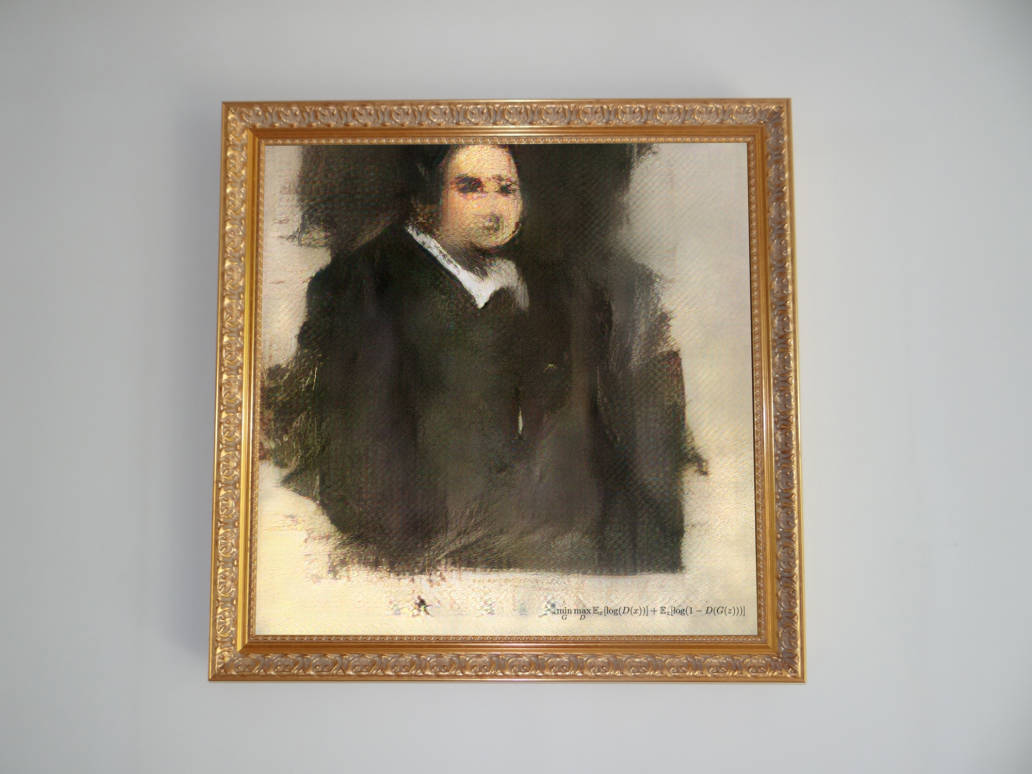
Further reading: GAN (Generative Adversarial Network) is a deep learning model commonly utilized in AI art. GANs have the ability to generate new data, such as images, text, music, and videos. They operate by employing two neural networks: a generator network and a discriminator network. The generator receives random input data and endeavors to produce new data that resembles the training data, while the discriminator's role is to differentiate between real and generated data.
During the training process, these two networks compete and learn from each other until the generator can generate synthetic data that is indistinguishable from real data.
As a research concept, GANs are accessible to developers and practitioners interested in machine learning. GANs have found application in various AI art technologies, including the aforementioned DeepDream algorithm. Google's research department, Google Brain, has been actively involved in advancing GAN research.
Additionally, Google's open-source deep learning framework, TensorFlow, provides valuable tools and resources for implementing GANs, making it widely embraced by researchers and practitioners within the GAN community.
What is AI art?

AI art, as the name suggests, encompasses artwork created or generated using artificial intelligence (AI) technology. It uses algorithms, machine learning models, and computational methods to generate or assist in creating visual, auditory, or other forms of artistic output.
AI art finds application in various artistic disciplines, such as visual arts, music, literature, and more. It aims to explore the intersection of AI and creativity, blurring the boundaries between human-generated and machine-generated art.
Several well-known AI art tools have emerged, including:
RunwayML: RunwayML is a software platform that offers a range of AI tools tailored for creative applications. It provides features such as AI-generated image synthesis, style transfer, text-to-image generation, and more. Artists and creators can leverage these tools to explore new possibilities in their artistic endeavors.
Google's DeepDream: DeepDream is a Google project that utilizes deep neural networks to generate surreal and dreamlike images. By enhancing patterns and features within input images, DeepDream produces visually complex and captivating results. Artists can use this tool to unleash their creativity and push the boundaries of traditional image creation.
OpenAI's DALL E: Developed by OpenAI, DALL E is a model that generates images based on text descriptions. By combining deep learning and language understanding, DALL E can create unique and imaginative visuals guided by provided text cues. This opens up new avenues for artists to transform their ideas into visual form.
NVIDIA's GauGAN: NVIDIA also tossed its hat in the AI game with GauGAN, an interactive AI tool that converts simple sketches into realistic images. It employs generative adversarial networks (GANs) to transform rough sketches into detailed and lifelike visuals. Artists can experiment and refine their artwork by harnessing the capabilities of this powerful tool.
ArtBreeder: ArtBreeder is an online platform that utilizes AI-driven generative algorithms. It allows users to combine and manipulate images to create new and unique artwork. By blending and evolving images, artists can explore innovative approaches and generate captivating compositions.
These well-known AI art tools exemplify the ongoing advancements at the intersection of AI and creativity. The tools serve as a creative playground where artists can explore, experiment, and push the boundaries of artistic expression.
How does AI art work?
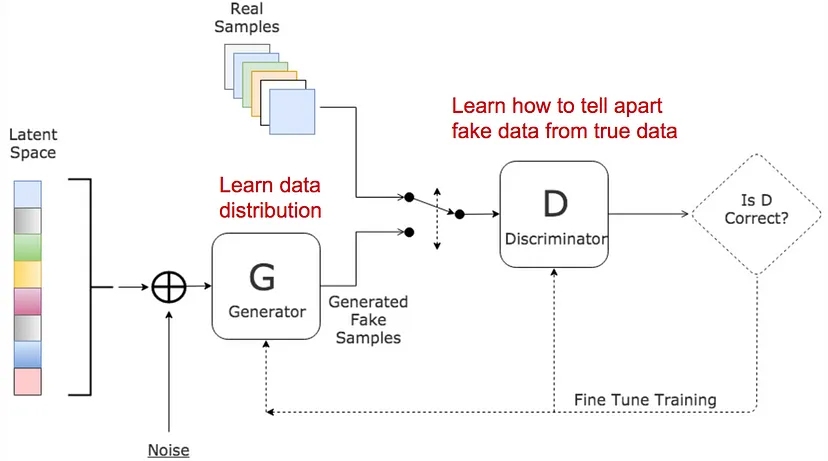
Understanding how AI achieves artistic creation, despite its requirement for creativity, can be both fascinating and unsettling. While it may seem reasonable for a robot to move or dance according to a fixed program, or for AI to generate formulaic articles, the ability of AI to create art raises questions about its creative process.
To shed light on this, let's explore the working principle of GAN mentioned earlier, as it serves as a glimpse into the workings of AI art.
GAN is one of the deep learning models utilized in AI art. Broadly speaking, the working principle of AI art shares similarities with GAN. It can be divided into the following four steps:
Data collection: Gathering data from various internet-based artworks, encompassing not only fine art paintings but also sketches, photographs, digital images, and more. This comprehensive dataset serves as the foundation for AI training.
Model training: After collecting the data, the next step involves training on this dataset. Different training models can be employed to recognize patterns, styles, and characteristics present in the artwork data, utilizing supervised or unsupervised learning processes.
Feature extraction: Once the features are identified, the AI model extracts high-level features from the training data. These features summarize the visual characteristics of the artwork, including color schemes, textures, shapes, compositions, and more.
Generation process: Following extensive training, the AI model can generate new works of art based on the learned features. The specifics of the generation process depend on the model being used. For instance, GAN is a widely employed generative model, and other commonly utilized generative models include Variational Autoencoders (VAE),Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), and more.
VAE: Variational Autoencoder is a model that learns compressed representations of training data and can generate new artwork by sampling from the learned data distribution. It enables the creation of diverse and unique artwork based on the learned patterns and features.
RNN: Recurrent Neural Network is a type of neural network that can generate continuous works of art by learning patterns and relationships between brush lines or stroke-by-stroke sketches. This enables the creation of artwork that exhibits a sense of coherence and flow.
By iterating and refining the output, artists and developers can generate artwork of different styles or concepts, enhancing the overall quality and creativity of the AI-generated pieces.
Will AI art replace human artists?
Although AI cannot directly generate ideas, it can even use data to simulate the process of the human brain conceiving ideas and do it better.
So will the work of artists be affected by AI?
The answer is a yes and a no, and it may vary from person to person.
The emergence of AI art has indeed brought new competition to the art market. Regardless of the artists, collectors, galleries, and sellers will be interested in AI-generated artwork, which may affect the demand for works created by artists to a certain extent.
Artists may need to tweak their strategies and explore new avenues to differentiate themselves, here are a few ways we recommend:
The emergence of AI art means new audiences and platforms for displaying works, which also require humans to control, learn, train and generate. If artists can use AI as a tool for creative experimentation, they may find their own unique niche and new job opportunities.
Artists may integrate AI technology into their artistic practice, after all, the breadth of technical knowledge mastered by AI tools and algorithms may be much greater than that of humans. Artists can use it to explore new technologies and push the boundaries of their creativity to improve their artistic output. It is worth mentioning that not all artists welcome this practice in the art industry, some artists may prefer to keep the traditional method, it depends on your personal choice.
Since AI tools can generate works very quickly, AI art can also serve as a well-defined and numerous source of creative inspiration, with which artists can explore and experiment with new ideas, styles, and concepts.
The shortcomings of AI art are obvious, that is, the lack of elements related to human nature behind it. Artists can start from this aspect and deliberately study and strengthen the unique voice, personal experience, and emotional connection behind the art, emphasizing its authenticity and emotional resonance, which may bring new demands to their works.
AI art VS Human art
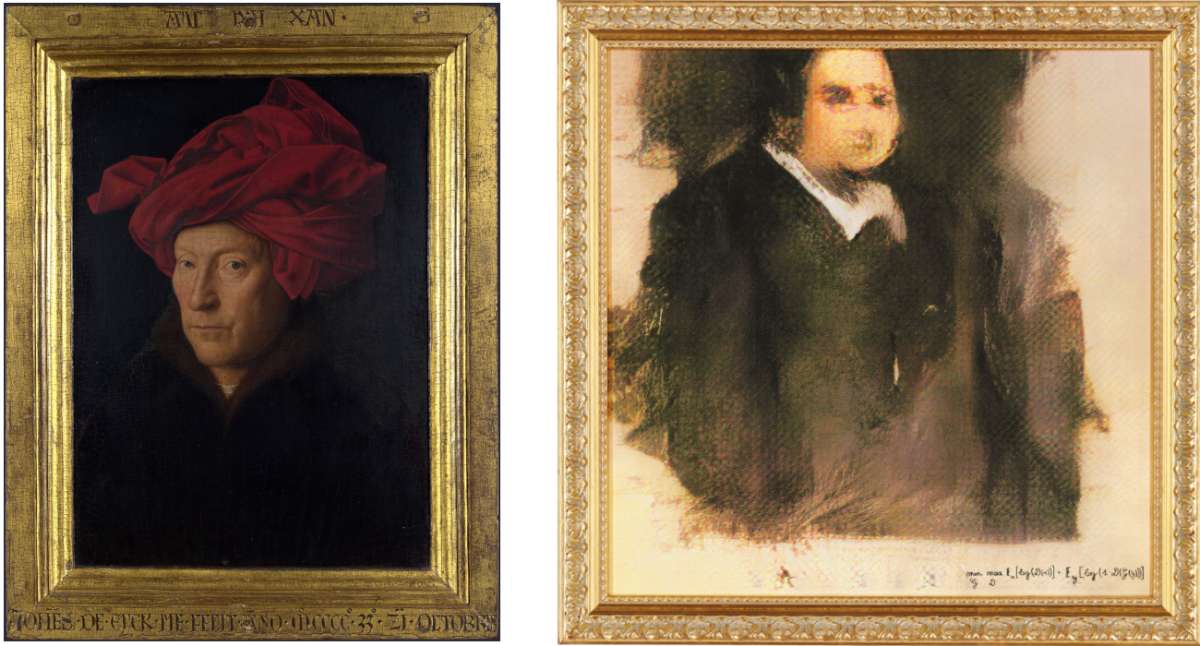

From the working principle of AI art, it is not difficult to see that the process of creating these creative works by AI does not involve the expression of creativity, emotion, and imagination like ordinary humans. Instead, it relies on the data from existing artworks and undergoes training, learning, and generating new works through the model. Think of it this way, the AI tools' capabilities will rely on how the artist uses them and their limitations are dependent on what it has "learned."
Such works have several disadvantages when compared to the works of human artists.
AI lacks life, personal experience, and emotions, which means it has no understanding of the content of its own works. It also misses the "human touch" and its nuances that stir the feelings of its human audience.
The interpretation of AI-generated artwork by the audience can be highly subjective, as anyone can express their own opinions.
In contrast, works created by human artists often incorporate the artist's personal emotions, experiences, and intentions. We can witness how artists integrate their unique perspectives and thoughts about the world into their art. Why? Because we also can relate and empathize as humans. Many artists draw inspiration from unique human experiences and at points, mirror the realities they live in.
Such works usually encompass human experiences, reflections on culture, social issues, personal narratives, and historical context.
Since AI-generated artworks heavily rely on training data and algorithms used during the creation process, they are limited in their ability to innovate. All AI art can be traced back to previous works because it is a combination of previously existing works fed into its algorithm.
Moreover, even though AI art learns from existing art, the works it creates lack the conscious intent and emotional depth possessed by human artists. AI-generated works are typically random combinations of learned data.
While they may initially appear visually interesting and novel, it is challenging to discern the underlying meaning or expression behind them. As a result, it is difficult for the audience to establish a deeper emotional resonance, and they are more inclined to seek visual stimulation.
Using digital tools to enhance human artistic expression
In the pursuit of exploring new technologies and pushing the boundaries of creativity, many artists have turned to digital art tools to enhance their artistic output. One highly regarded tool in the artistic community is the XPPen Artist Pro 22, a flagship model from XPPen's lineup of graphic tablets. The XPPen Artist Pro 22 offers artists a seamless interface for creating stunning digital artworks with precision and fluidity. Its 21.5-inch full HD display provides a vibrant and immersive drawing experience, enabling artists to embrace the world of digital art and expand their creative capabilities.
With 8,192 levels of pressure sensitivity and support for tilt recognition, the XPPen Artist Pro 22 allows artists to achieve precise and natural pen strokes, simulating the feel of traditional art mediums. The tablet's ergonomic design ensures comfort during long drawing sessions, while its customizable shortcut keys offer quick access to frequently used functions, streamlining the creative process.
By harnessing the power of the XPPen Artist Pro 22, artists can unlock new possibilities, seamlessly blending traditional art techniques with the convenience and versatility of digital mediums. Whether sketching, painting, or illustrating, this advanced graphic tablet empowers artists to bring their visions to life with unparalleled precision and control.
What's your take in AI art? Do you believe AI will replace artists? Share your thoughts in the comments!
About Us
Originated from 2005, XPPen is now one of the top brands under HANVON UGEE, integrated with digital drawing products, content and service as a globally notable digital brand of digital art innovation.
Learn more